Raja Ampat archipelago in West Papua is home to Indonesia’s largest population of reef manta rays, Mobula alfredi. They are not mammals, but cartilaginous fish that are related to sharks.
This species is characterised by late maturation and extremely low fertility, which make their populations especially vulnerable. Males start to sexually mature at 9 to 13 years old, while females require 13 to 17 years to mature. A female gives birth to only one pup every 2 to 6 years after about one year of pregnancy.
Their populations have been depleted due to overfishing in many regions in Indo-Pacific. Some of these include East Nusa Tenggara and North Sulawesi (Indonesia), the Philippines, Papua New Guinea and Mozambique in Africa.
In Raja Ampat, there were anecdotal reports from the local community suggesting that reef manta rays were often caught unintentionally by non-local shark fishers. In the 1990s and early 2000s, sharks were heavily caught in Raja Ampat using large gillnets and longlines, not to mention other illegal and destructive fishing practices by outsiders.
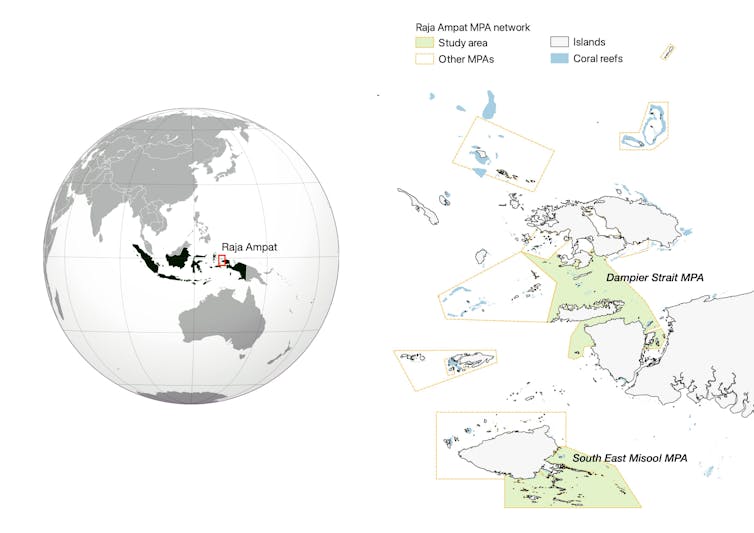
To protect marine biodiversity and ensure food security for local communities, the Raja Ampat government officially developed a marine protected area network in 2007. Since then, manta rays in the region have begun to enjoy some protection. After 15 years of this initiative, its impact on manta ray populations had not been assessed.
Our new research, published in Frontiers in Marine Science, found reef manta ray populations in Raja Ampat have thrived over a decade of our study. This study suggests that the long-term implementation of conservation and management efforts implemented by Raja Ampat government has been fruitful.
Our research is the first in the world to report thriving populations of this megafauna. It also provides a reason for optimism when an integrated approach is adopted for shark and ray conservation initiatives.
Assessing two growing populations
Our research team managed to collect and curate manta ray images and sighting data from 2009 to 2019, thanks to citizen scientists and collaborators – especially divers and dive operators who contributed their manta ray photos.
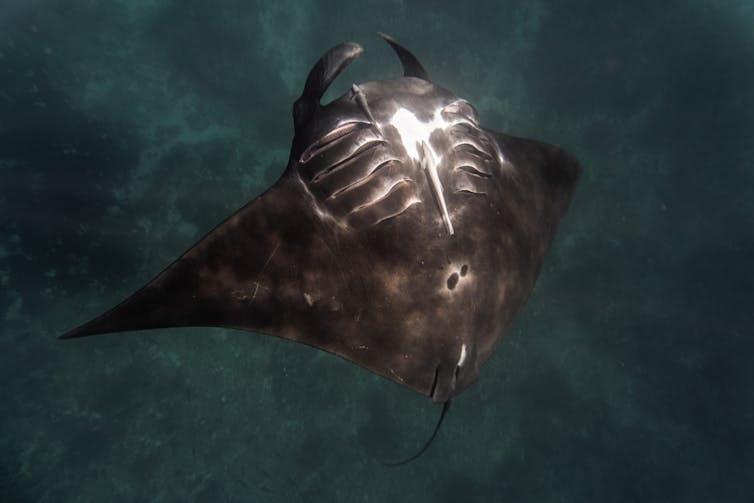

We used the sighting data to look into reef manta ray demographic trends in two marine protected areas with the most consistent data collection over a decade: Dampier Strait and South East Misool.
In Dampier Strait, the estimated population increased from 226 to 317, with an annual compound growth rate of 3.9%. South East Misool’s population increased at a higher rate of 10.7% per year, from 210 to 511 individuals over a decade of study.
The manta rays were estimated to have high survival rates. Each year, up to 93% of individuals in the populations survived. Furthermore, the populations typically saw a 20% boost from new individuals annually, which can be from newborns and/or larger rays from outside study areas. These resulted in the increase in manta ray populations in both marine protected areas.
Contributing factors
The thriving populations of reef manta rays strongly suggest this species is well protected in Raja Ampat waters. Almost all known feeding and cleaning sites are located within the 2 million hectare marine protected area network. These sites, where manta rays frequently visit and gather for feeding and to be cleaned of parasites by cleaner fish, are important for their survival and health.
We also found that El Niño events generated more intense upwellings (upward motion of seawater) – bringing cold and nutrient-rich water to the surface. These then increased opportunities for manta rays to feed in large feeding groups, enabling the manta rays to store much energy for reproduction and for mating.
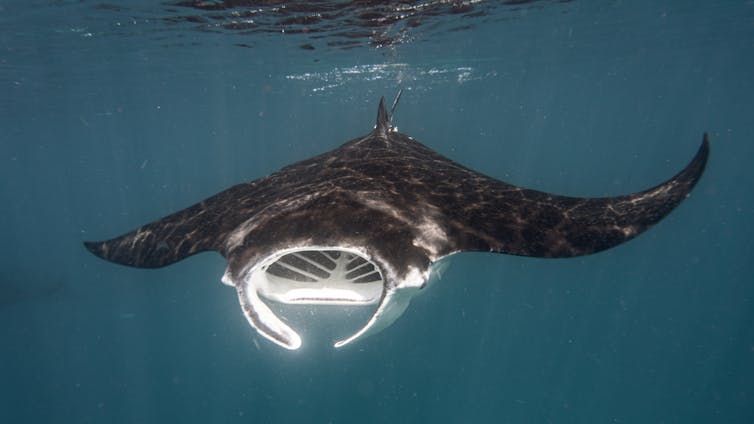

During and shortly after the El Niño events, we observed high number of pregnant rays in the populations. Following this period, many of the expected baby manta rays likely live in sheltered nursery areas like Wayag lagoon or Fam Islands, both situated in Raja Ampat. They stay there for a few years – which could increase their chance of survival – before they are large enough to join adult populations, like those in the study areas.
Lessons learned
This research shows that it is not impossible to conserve large and highly migratory species such as reef manta rays. The series of conservation and management efforts implemented since 2007 by the Raja Ampat government has successfully minimised fisheries-related threats to manta ray populations.
The creation of a network of nine marine protected areas actively patrolled by local communities and authorities have forced sharks fishers to relocate to areas outside Raja Ampat, or change their livelihood. The use of fishing gear like gillnets and longlines has been restricted throughout Raja Ampat waters. All of these have minimised shark fishing and the resulting potential of manta rays unintentionally being caught.
Furthermore, the designation of Southeast Asia’s first shark and ray sanctuary in 2012 has given significantly stronger protection to manta rays. In the sanctuary, the vast development of manta tourism have pushed down fisheries-related threats to manta rays to minimal.
Finally, favourable environmental conditions affected by the El Niño events have helped manta rays continue to thrive.
What’s next?
Given massive efforts to monitor the vast and remote areas of Raja Ampat archipelago, continued monitoring efforts and contributions from citizen scientists for the growing manta sighting database are required.
It is also important to maintain the conservation efforts to minimise threats, allowing manta ray populations to survive and thrive.
Edy Setyawan, Marine Ecologist, University of Auckland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.











